Decoding the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and Its Impact on Textile Exports
What Is CBAM and Why It Matters
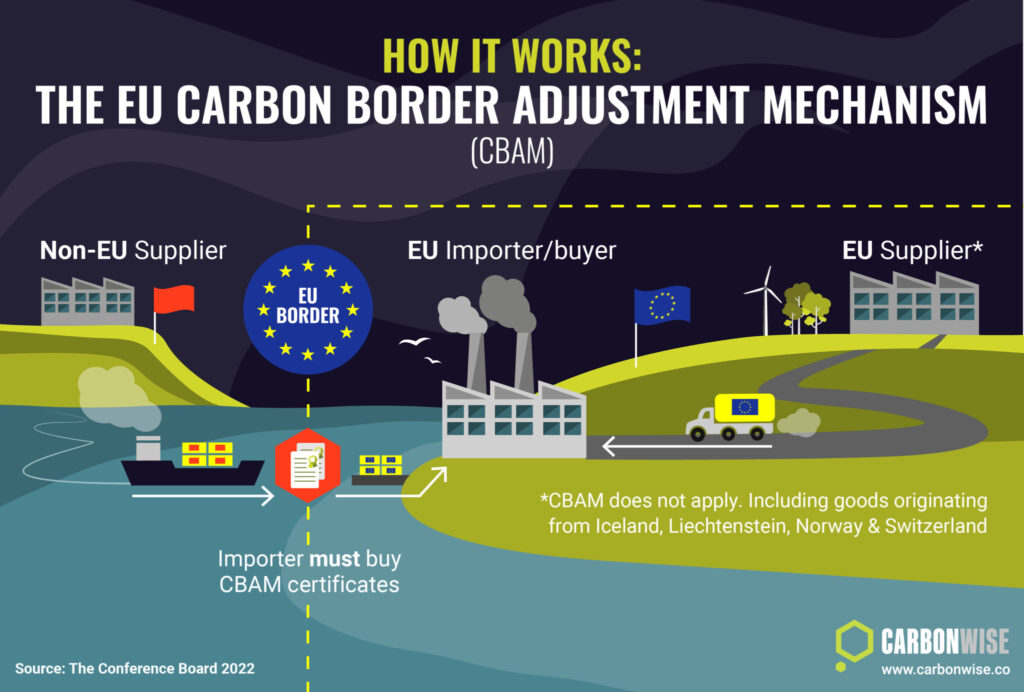
The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) is one of the most significant trade policies of the decade. While it currently targets sectors like cement, steel, and fertilizer, its impact will eventually extend to energy-intensive industries including textiles.
CBAM’s intent is to prevent “carbon leakage” by imposing carbon tariffs on imports produced with higher emissions than EU standards. For textile exporters, this means that carbon efficiency will soon become as critical as product quality.
Implications for Indian Textile Exporters
India, as one of the largest exporters of yarn and fabric to Europe, will inevitably feel CBAM’s ripple effects.Exporters must prepare for detailed emission reporting and verification. Mills relying on coal or heavy fossil fuels may face penalties, while those adopting solar, wind, or biomass energy will gain a pricing advantage.
Companies like Ascento Overseas are already anticipating this shift by collaborating with energy-efficient mills and promoting responsible sourcing. This early adaptation will translate into long-term competitiveness in regulated markets.
Turning Compliance into Opportunity
CBAM can be seen as a barrier or a bridge.While some exporters may struggle with new compliance costs, forward-thinking ones can leverage it as proof of sustainability leadership. Demonstrating a lower carbon footprint will help command premium prices and access preferential buyer networks.
The Path Forward
The textile industry must integrate carbon tracking into its supply chain management systems. Digital tools, supplier audits, and lifecycle assessments will soon become standard practice.
Those who prepare now will not only meet future regulations but also win the trust of environmentally conscious buyers. The future of exports is not just about “Made in India” – it is about Responsibly Made in India.
